The page is available only when the Docker plugin is enabled on the Settings/Preferences | Plugins page as described in Managing plugins.
- #Webstorm Dockerized Launch webstorm through a docker container. Docker; Docker-compose; Need to be on Linux; using docker-compose. Git clone; docker-compose up -d; If all went well, webstorm should launch. You'll either be asked to import webstorm settings or use the existing ones located in your home directory. Potential issues.
- This project is a simple Docker image that runs JetBrains IntelliJ IDE. A working Docker engine; a working Docker Compose installation; Building. Type docker-compose build to build the image. Docker will automatically install the newly built image into the cache.
With Docker Desktop running on WSL 2, users can leverage Linux workspaces and avoid having to maintain both Linux and Windows build scripts. In addition, WSL 2 provides improvements to file system sharing, boot time, and allows access to some cool new features for Docker Desktop users. With WebStorm 2016.3, Docker is added to the list of remote interpreter options. Once configured, WebStorm will create a new container on each run, with the container bound to the project directory, then execute your project code in the Docker-based Node.js environment.
Specify the settings for accessing the Docker API. For more information about using the Docker integration with WebStorm, see Docker.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the configuration. |
| Connect to Docker daemon with | Select the method for connecting to the Docker API.
|
| Path mappings | For Windows and macOS: Specify the mappings for folders that can be shared between the host and the container volumes. Use to edit an existing mapping, or to create a new one.
|
Debugging a project that runs in a Docker container can be tough! This guide runs through debugging a Typescript project (Nestjs) using Webstorm and docker. Although the guide uses Nestjs as the framework and Webstorm as the IDE, it should work in general for any IDE and any Typescript project.
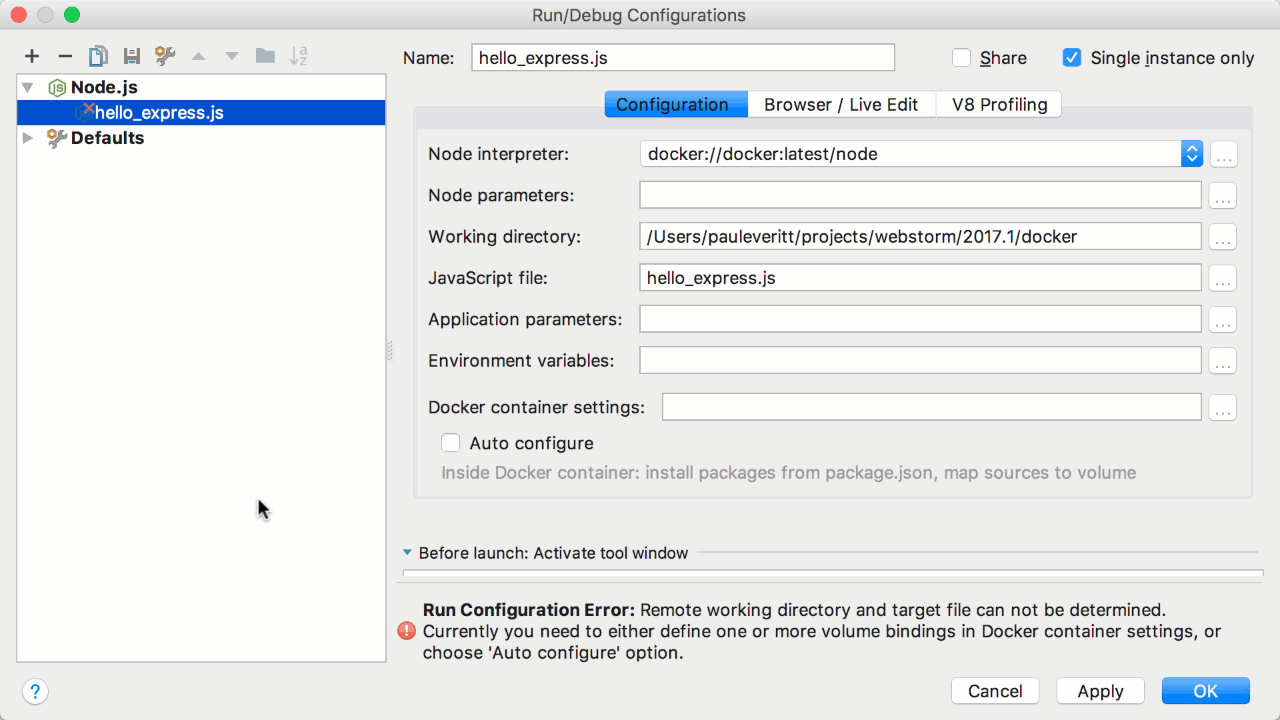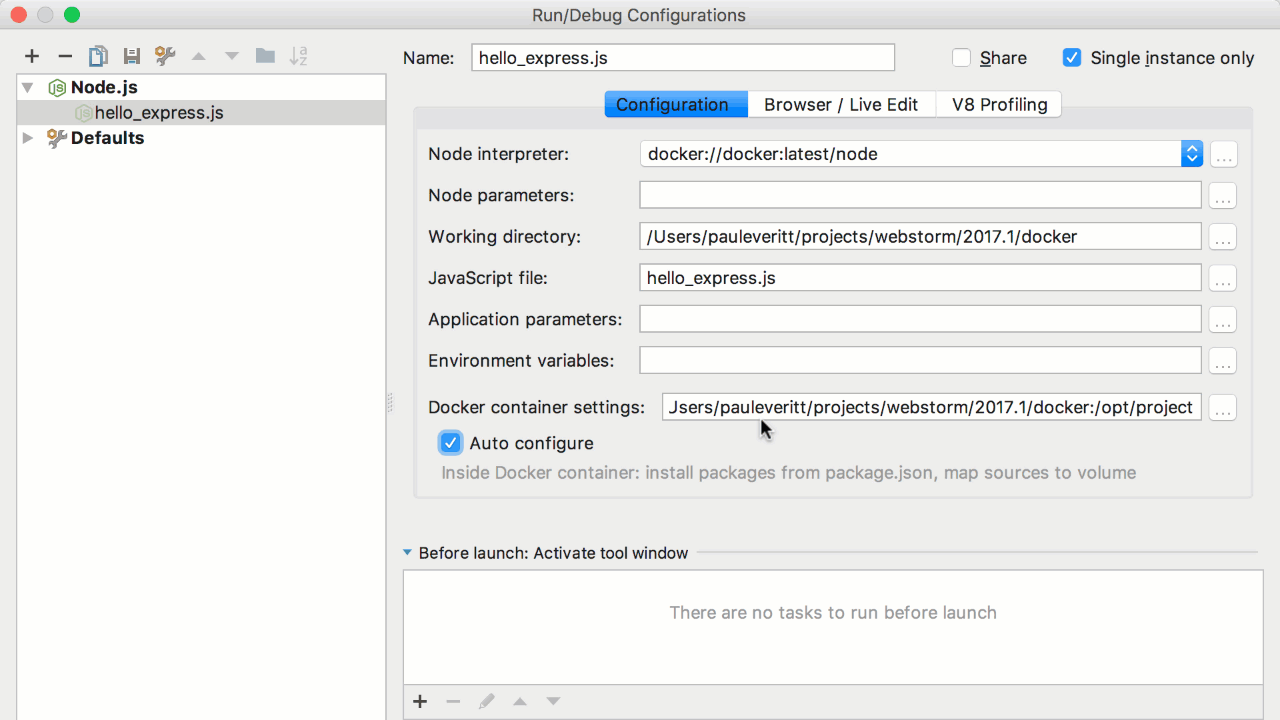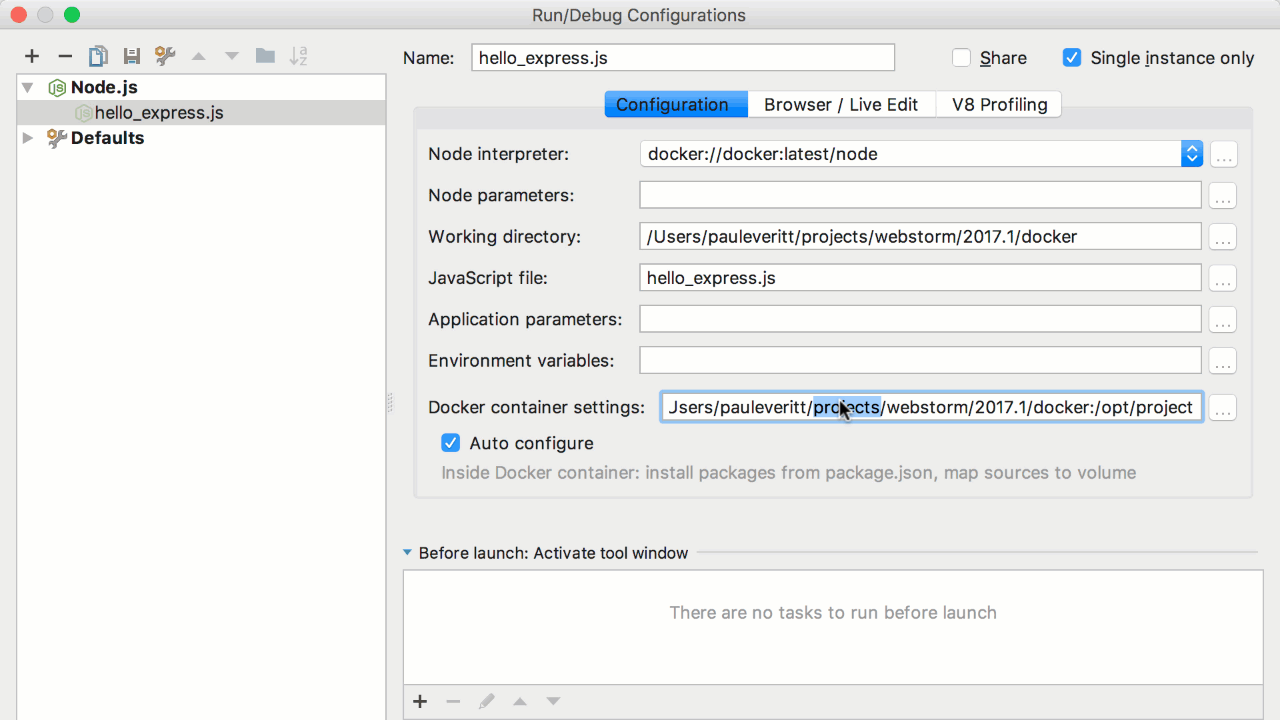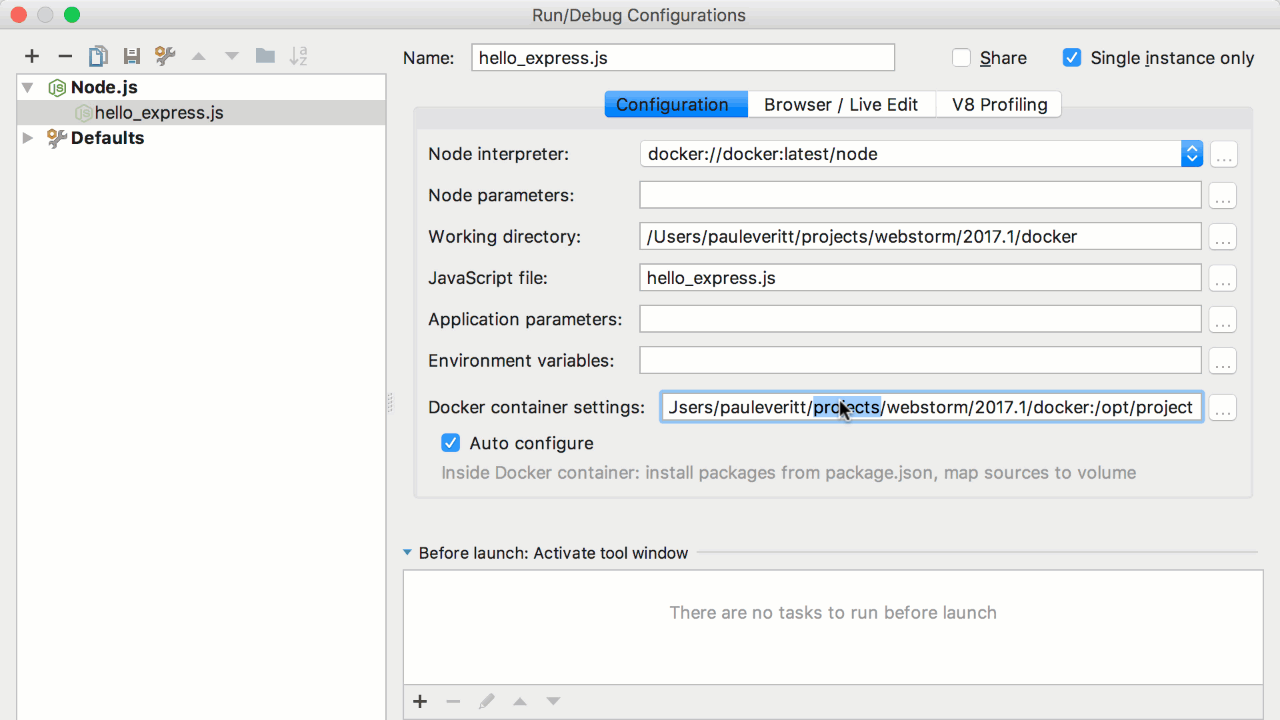
I've recently been looking at how people debug Typescript applications. It's pretty straight forward, all you have to do is set up the execution script in Webstorm (or any IDE really) and you're good to go.. The problem is that that solution assumes we are running the application directly off our PCs. We use docker for our development environment to ensure that there is a fast setup. Furthermore, we use docker-compose Sketchup 3d for mac. , to set up the full stack for local development. This means that the current solutions out there won't work for us, unless we want to run half of the stack through docker-compose and the other half directly on our PCs.
So I started reading around and found that there are ways to bind to the debug ports for node projects. The tutorials were great but I couldn't find one that explained the process from start to finish, this article was what I worked off to get to this answer. This article outlines how to set up debugging in a Typescript project that runs using docker containers. I've used nest as our framework since that's what is most applicable in our use cases.
If you'd like to follow in the example, you can clone the GitHub repository. As long as you have docker and docker-compose installed, it should all work!
I'm using a nest project and I've placed the code into a backend folder. You'll also see a devops folder where I keep the docker-compose.yaml file and the Dockerfile that should be used to build the backend code.
Finally, I bind the backend/src directory into the docker container so that changes are picked up by nodemon during development and there's a quick project rebuild and restart without having to restart the docker container.
So currently, my docker-compose.yaml and Dockerfile look as follows,
You'll notice that I bind port 9229 in my docker-compose.yaml file, this will be very applicable in the next steps so don't forget it! For future comparison, this is what the package.json and nodemon.json files look like in the backend folder before I set up the debugger,
Cool so we're set up with the docker-compose.yaml and Dockerfile and if you run docker-compose up --build you should see the system build and start up. The next step is to configure our package.json and nodemon.json files to allow for debugging. Instead of using ts-node directly (which is what we do for a lot of Typescript projects), we should rather start up node normally and register the ts-node module.

In the nodemon.json file, the command for execution is currently ts-node -r tsconfig-paths/register src/main.ts. We need to change this to start with node and then we can add some debugging flags. We're going to use the --inspect option in node to allow us to access the debugging information. If you haven't heard of inspect before, take a look at the official documentation for full details.
The command for execution should change from the above command to the following, node --inspect=0.0.0.0 --require ts-node/register --require tsconfig-paths/register src/main.ts. Meaning that our nodemon.json file now looks as follows,
That's all we need in our project to allow for our debugger to intercept and stop the code at breakpoints we set. So the next step is to set up our IDE (in my case, Webstorm) to utilise this setup.
As mentioned previously, I am binding port 9229 in the docker container to port 30000 on my local machine. This is the port that I need to set the IDE debugger to listen on.
In Webstorm, click on the Add Configuration.. option on the top right,
Microsoft lync. Click on the + symbol above templates so that we can create our own custom template.
Select the Attach to Node.js/Chrome option,
You should now see the following window,
The default settings point to port 9229, but I bind port 9229 in the docker-compose system to port 30000 so we need to change this port to 30000. Make the following changes below and save the new template,
Cool, now we're ready to go! Start up the debugger by clicking the green bug in the top right,
I then changed my backend/src/app.service.ts file to generate a few random numbers and sum them up, Video downloading software for mac.
Now if you were to run docker-compose (you'd go into the devops folder and run docker-compose up --build) you could open up your browser and navigate to localhost:3000 and you'd see output like this,
The next step is to add breakpoints in the app.service.ts file. Click on the left next to one of the line numbers to add a breakpoint,
Now refresh the tab that has localhost:3000 open and check on Webstorm and you should see that it has stopped at that breakpoint,
If it didn't break at that point then rerun the debugger by clicking the green bug or curved arrow on the bottom left of the window,
Webstorm Docker Node_modules
Refresh the localhost:3000 page again and it should be working.
Webstorm Docker-compose Debug
And that's it, you're now able to debug Typescript projects running in docker containers using Webstorm (or any IDE of your choice). Debugging using tools like this makes finding issues a lot faster (especially compared to console logging everything) so I'd definitely recommend setting it up!
