In writing the electron configuration for Magnesium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for magnesium go in the 2s orbital. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. The first person to recognise that magnesium was an element was Joseph Black at Edinburgh in 1755. He distinguished magnesia (magnesium oxide, MgO) from lime (calcium oxide, CaO) although both were produced by heating similar kinds of carbonate rocks, magnesite and limestone respectively. Magnesium is an alkaline earth metal and is the second element located in the second row of the periodic table. It is the eighth most abundant element on Earth. Magnesium atoms have 12 electrons and 12 protons. There are two valence electrons in the outer shell. Characteristics and Properties. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Magnesium is 12. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom. As you know, this happens when an atom has 8 electrons, also called valence electrons, in its outermost energy shell, i.e. When the atom has a complete octet. Now, magnesium, Mg, has 2 valence electrons. In order to complete its octet, it must get to 8 valence electrons.
- Magnesium Electrons
- Magnesium Electrons In Outer Shell
- Magnesium Protons Neutrons And Electrons
- Magnesium Electrons In Outer Shell
- Magnesium Electrons Protons Neutrons
- Magnesium Electron Configuration Full
- Magnesium Electrons Configuration

How many electrons in magnesium share the quantum numbers #l=0# and #m_l = 1# ?
1 Answer
Explanation:
As you know, four quantum numbers are used to describe the position and spin of an electron in an atom.
Your goal here is to identify how many electrons located in an atom of magnesium,
Start by writing the complete electron configuration for a neutral atom of magnesium. Magnesium is located in period 3, group 2 of the periodic table and has an atomic number equal to
This means that a neutral magnesium atom will have a total of
Now, the angular momentum quantum number,
# l = 0 -># the s-subshell#l = 1 -># the p-subshell#l=2 -># the d-subshell#l =3 -># the f-subshell#vdots#
In your case, the value
Now, the magnetic quantum number,
The only possible value for
You can thus say that no electrons share the quantum numbers
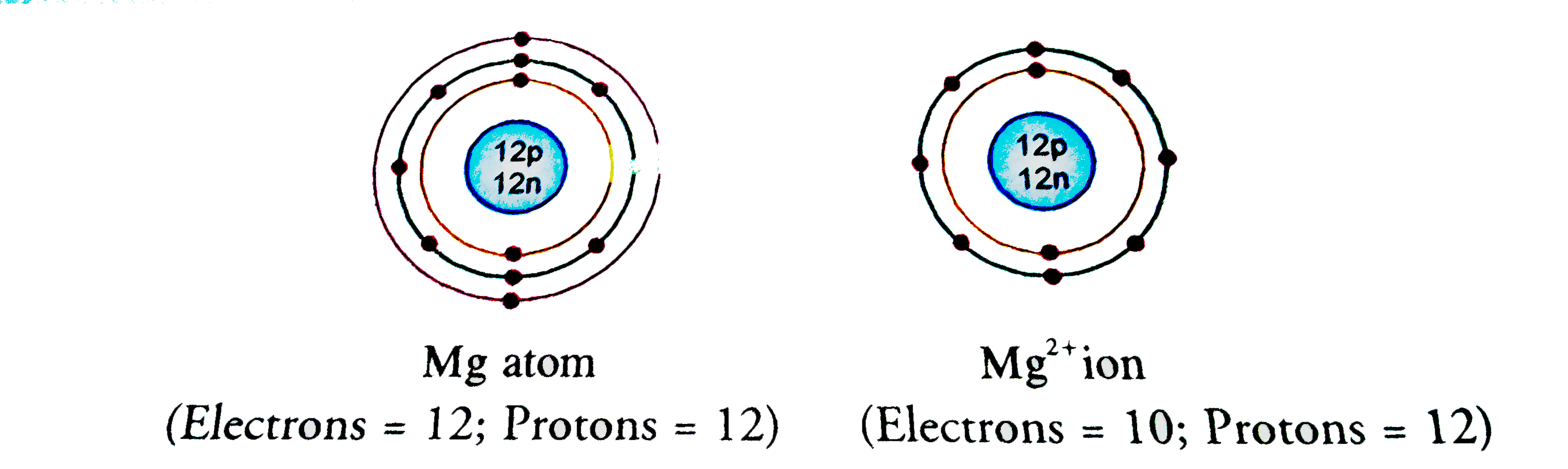
You will never find an atom in which an electron has the quantum number
ALTERNATIVE INTERPRETATION
Just in case you had to determine how many electrons share the quantum number
If you're looking for electrons that have

#1s^2 -># two electrons located in the s-subshell of the first energy level#2s^2 -># two electrons located in the s-subshell of the second energy level#3s^2 -># two electrons located in the s-subshell of the third energy level
Therefore, a total of six electrons have
Now, in a magnesium atom,
More specifically, you have
#m_l = -1 -># the#p_x# orbital#m_l = color(white)(-)0 -># the#p_y# orbital#m_l = color(white)(-)1 -># the#p_z# orbital
A magnesium atom has the p-subshell of the second energy level completely filled with electrons, which means that the
Therefore, a total of two electrons have
Related questions
The key difference between beryllium and magnesium is that beryllium atom has two energy levels containing its electrons, whereas magnesium atom has three energy levels containing its electrons.
Beryllium and magnesium are two adjacent alkaline earth metals. That means; both these chemical elements are in the same group (group 2), but in different periods, i.e., beryllium is in the 2nd period while magnesium is in the 3rd period.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Beryllium
3. What is Magnesium
4. Side by Side Comparison – Beryllium vs. Magnesium in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Beryllium?
Beryllium is a chemical element having atomic number 4 and symbol Be. It appears as a shiny grey solid at standard temperature and pressure. Relatively, this element is rare in the universe. It is a divalent element. That means; it can from the +2 oxidation state via removing two of its electrons in the valence shell. The electron configuration of beryllium is [He]2s2. Therefore, it does not have p or d orbitals filled electrons. Hence, it is an s-block element.
Beryllium is a hard metal that is brittle as well. It has a close-packed hexagonal crystal system. The stiffness of this metal is exceptional. Moreover, it has a high specific heat and thermal conductivity. While bonded to other atoms, beryllium has a high atomic and ionic radius because it has a very high ionization potential and a strong polarization.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a chemical element having atomic number 12 and symbol Mg. It occurs as a gray-shiny solid at room temperature. Magnesium is in group 2, period 3 in the periodic table. Therefore, it is an s-block element. It is also an alkaline earth metal (group 2 chemical elements are named as alkaline earth metals). The electron configuration of magnesium is [Ne]3s2.
Magnesium Electrons
Figure 02: Magnesium
Magnesium is an abundant chemical element in the universe. In nature, it occurs in combination with other chemical elements. Here, the oxidation state of magnesium is +2. The free metal is highly reactive, but we can produce it as a synthetic material. It can burn, producing very bright light. We call it a brilliant white light. We can obtain magnesium by electrolysis of magnesium salts. These magnesium salts can be obtained from brine.
Magnesium is a lightweight metal, and it has the lowest values for melting and boiling points among alkaline earth metals. Also, this metal is brittle and easily undergoes fracture along with shear bands. When it is alloyed with aluminum, the alloy becomes very ductile.
When exposed to air, magnesium tarnishes. It also does not require an air-free storage space because a thin layer of magnesium oxide protects its surface. And, this magnesium oxide layer is impermeable and is difficult to remove as well.
Magnesium Electrons In Outer Shell
The reaction between magnesium and water is not as rapid as calcium and other alkaline earth metals. When we submerge a piece of magnesium in water, we can observe hydrogen bubbles emerge from the metal surface. However, the reaction speeds up with hot water. Moreover, this metal can react with acids exothermally, e.g., hydrochloric acid (HCl).
What is the Difference Between Beryllium and Magnesium?
Beryllium and magnesium are two chemical elements in the same group, but two adjacent periods. Beryllium is a chemical element having atomic number 4 and symbol Be, while Magnesium is a chemical element having the atomic number 12 and symbol Mg. The key difference between beryllium and magnesium is that beryllium atom has two energy levels containing its electrons, whereas magnesium atom has three energy levels containing its electrons.
Moreover, the magnesium metal has the lowest melting and boiling points among alkaline earth metals; therefore, the melting and boiling points of beryllium is higher than magnesium. Apart from that, another difference between beryllium and magnesium is that beryllium is diamagnetic, while magnesium is paramagnetic.

Summary – Beryllium vs Magnesium
Magnesium Protons Neutrons And Electrons
Beryllium and magnesium are two chemical elements in the same group, but two adjacent periods. The key difference between beryllium and magnesium is that beryllium atom has two energy levels that contain its electrons, whereas magnesium atom has three energy levels containing its electrons.
Magnesium Electrons In Outer Shell
Reference:
Magnesium Electrons Protons Neutrons
1. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. “Magnesium Facts (Mg or Atomic Number 12).” ThoughtCo, Aug. 2, 2019, Available here.
Magnesium Electron Configuration Full
Image Courtesy:
Magnesium Electrons Configuration
1. “Be-140g” By Alchemist-hp = Alchemist-hp (pse-mendelejew.de) – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “CSIRO ScienceImage 2893 Crystalised magnesium” By CSIRO (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
Related posts:
