SSH.com frontpage. For configuring passwordless public key authentication, see ssh-keygen. The ssh program on a host receives its configuration from either the command line or from configuration files /.ssh/config and /etc/ssh/sshconfig. Command-line options take precedence over configuration files. The user-specific configuration file /.ssh/config is used next. Ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 This will generate the SSH key. Press Enter at the following prompt to save the key in the default location (under your user directory as a folder named.ssh). You will then be prompted to enter a secure passphrase, but you can leave that blank. It's a free, simple, and easy-to-use tool. Terminus is a free and open source software with clean and modern UI, as opposed to numerous proprietary SSH clients out there with an outdated and unintuitive interface. Uses a lot of computer's memory.
SSH client & key policies
paramiko.client.AutoAddPolicy¶Policy for automatically adding the hostname and new host key to thelocal HostKeys object, and saving it. This is used by SSHClient.
paramiko.client.MissingHostKeyPolicy¶
Interface for defining the policy that SSHClient should use when theSSH server’s hostname is not in either the system host keys or theapplication’s keys. Pre-made classes implement policies for automaticallyadding the key to the application’s HostKeys object (AutoAddPolicy),and for automatically rejecting the key (RejectPolicy).
This function may be used to ask the user to verify the key, for example.
__weakref__¶list of weak references to the object (if defined)
missing_host_key(client, hostname, key)¶Called when an SSHClient receives a server key for a server thatisn’t in either the system or local HostKeys object. To acceptthe key, simply return. To reject, raised an exception (which willbe passed to the calling application).
paramiko.client.RejectPolicy¶Policy for automatically rejecting the unknown hostname & key. This isused by SSHClient.
paramiko.client.SSHClient¶A high-level representation of a session with an SSH server. This classwraps Transport, Channel, and SFTPClient to take care of mostaspects of authenticating and opening channels. A typical use case is:
You may pass in explicit overrides for authentication and server host keychecking. The default mechanism is to try to use local key files or anSSH agent (if one is running).
Instances of this class may be used as context managers.
New in version 1.6.
__init__()¶Create a new SSHClient.
close()¶Close this SSHClient and its underlying Transport.
Warning
Failure to do this may, in some situations, cause your Pythoninterpreter to hang at shutdown (often due to race conditions).It’s good practice to close your client objects anytime you’redone using them, instead of relying on garbage collection.
connect(hostname, port=22, username=None, password=None, pkey=None, key_filename=None, timeout=None, allow_agent=True, look_for_keys=True, compress=False, sock=None, gss_auth=False, gss_kex=False, gss_deleg_creds=True, gss_host=None, banner_timeout=None, auth_timeout=None, gss_trust_dns=True, passphrase=None, disabled_algorithms=None)¶Connect to an SSH server and authenticate to it. The server’s host keyis checked against the system host keys (see load_system_host_keys)and any local host keys (load_host_keys). If the server’s hostnameis not found in either set of host keys, the missing host key policyis used (see set_missing_host_key_policy). The default policy isto reject the key and raise an SSHException.
Authentication is attempted in the following order of priority:

- The
pkeyorkey_filenamepassed in (if any)key_filenamemay contain OpenSSH public certificate pathsas well as regular private-key paths; when files ending in-cert.pubare found, they are assumed to match a privatekey, and both components will be loaded. (The private keyitself does not need to be listed inkey_filenameforthis to occur - just the certificate.)
- Any key we can find through an SSH agent
- Any “id_rsa”, “id_dsa” or “id_ecdsa” key discoverable in
~/.ssh/- When OpenSSH-style public certificates exist that match anexisting such private key (so e.g. one has
id_rsaandid_rsa-cert.pub) the certificate will be loaded alongsidethe private key and used for authentication.
- When OpenSSH-style public certificates exist that match anexisting such private key (so e.g. one has
- Plain username/password auth, if a password was given
If a private key requires a password to unlock it, and a password ispassed in, that password will be used to attempt to unlock the key.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Raises: |
|
| Raises: |
|
| Raises: |
|
| Raises: | socket.error – if a socket error occurred while connecting |
Changed in version 1.15: Added the banner_timeout, gss_auth, gss_kex,gss_deleg_creds and gss_host arguments.
Changed in version 2.3: Added the gss_trust_dns argument.
Changed in version 2.4: Added the passphrase argument.
Changed in version 2.6: Added the disabled_algorithms argument.
exec_command(command, bufsize=-1, timeout=None, get_pty=False, environment=None)¶Execute a command on the SSH server. A new Channel is opened andthe requested command is executed. The command’s input and outputstreams are returned as Python file-like objects representingstdin, stdout, and stderr.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: | the stdin, stdout, and stderr of the executing command, as a3-tuple |
| Raises: |
|
get_host_keys()¶Get the local HostKeys object. This can be used to examine thelocal host keys or change them.
| Returns: | the local host keys as a HostKeys object. |
|---|
get_transport()¶Return the underlying Transport object for this SSH connection.This can be used to perform lower-level tasks, like opening specifickinds of channels.
| Returns: | the Transport for this connection |
|---|
invoke_shell(term='vt100', width=80, height=24, width_pixels=0, height_pixels=0, environment=None)¶Start an interactive shell session on the SSH server. A new Channelis opened and connected to a pseudo-terminal using the requestedterminal type and size.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: | a new |
| Raises: |
|
load_host_keys(filename)¶Load host keys from a local host-key file. Host keys read with thismethod will be checked after keys loaded via load_system_host_keys,but will be saved back by save_host_keys (so they can be modified).The missing host key policy AutoAddPolicy adds keys to this set andsaves them, when connecting to a previously-unknown server.
This method can be called multiple times. Each new set of host keyswill be merged with the existing set (new replacing old if there areconflicts). When automatically saving, the last hostname is used.
| Parameters: | filename (str) – the filename to read |
|---|---|
| Raises: | IOError – if the filename could not be read |
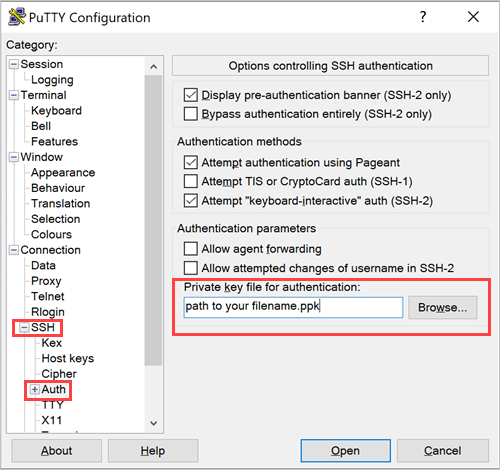
load_system_host_keys(filename=None)¶Configure Ssh Key
Load host keys from a system (read-only) file. Host keys read withthis method will not be saved back by save_host_keys.
This method can be called multiple times. Each new set of host keyswill be merged with the existing set (new replacing old if there areconflicts).
If filename is left as None, an attempt will be made to readkeys from the user’s local “known hosts” file, as used by OpenSSH,and no exception will be raised if the file can’t be read. This isprobably only useful on posix.
| Parameters: | filename (str) – the filename to read, or None |
|---|---|
| Raises: | IOError –if a filename was provided and the file could not be read |
open_sftp()¶Open an SFTP session on the SSH server.
| Returns: | a new SFTPClient session object |
|---|
save_host_keys(filename)¶Save the host keys back to a file. Only the host keys loaded withload_host_keys (plus any added directly) will be saved – not anyhost keys loaded with load_system_host_keys.
Open Ssh Key Client
| Parameters: | filename (str) – the filename to save to |
|---|---|
| Raises: | IOError – if the file could not be written |
set_log_channel(name)¶Set the channel for logging. The default is 'paramiko.transport'but it can be set to anything you want.
| Parameters: | name (str) – new channel name for logging |
|---|
set_missing_host_key_policy(policy)¶Set policy to use when connecting to servers without a known host key.
Specifically:
- A policy is a “policy class” (or instance thereof), namely somesubclass of
MissingHostKeyPolicysuch asRejectPolicy(thedefault),AutoAddPolicy,WarningPolicy, or a user-createdsubclass. - A host key is known when it appears in the client object’s cachedhost keys structures (those manipulated by
load_system_host_keysand/orload_host_keys).
| Parameters: | policy (MissingHostKeyPolicy) – the policy to use when receiving a host key from apreviously-unknown server |
|---|
paramiko.client.WarningPolicy¶Policy for logging a Python-style warning for an unknown host key, butaccepting it. This is used by SSHClient.

